Unveiling the Future of Telemedicine: 2023 Trends
Telemedicine is transforming the healthcare industry by offering remote medical care and consultation through the use of technology. It’s projected to be a major player in the healthcare market, with a global market size valued at a staggering $83.5 billion in 2022. But the industry is not slowing down anytime soon, with an estimated compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 24.0% from 2023 to 2030.
As the field continues to rapidly grow, it presents the potential to increase access to healthcare services while reducing the costs of providing care. Our analytical report on telemedicine examines 47,883 data sources, including patent filings, investments, and top companies, to assess the field’s evolution and future prospects.
Introduction to Telemedicine
Although telemedicine has been around since the early 1900s when doctors utilized telegraphs to communicate with patients in far-flung regions, the field has seen remarkable growth in recent times due to technological advancements.
Today, telemedicine encompasses an array of technologies such as videoconferencing, remote monitoring devices, and mobile applications. This allows patients to receive medical care and consultation from distant locations, which is particularly advantageous for those residing in rural or underserved areas.
Additionally, it can also cater to patients who are unable to travel outside their homes due to illness or disability. It’s especially beneficial for individuals who live in rural or underserved areas. Telemedicine can also be used to provide care to patients who are unable to leave their homes due to illness or disability.
Intellectual Property Trends
Several intellectual property (IP) concerns arise from the utilization of technology in telemedicine. These concerns pertain to safeguarding the technologies employed in telemedicine and ensuring the safety and effectiveness of healthcare services delivered through it.
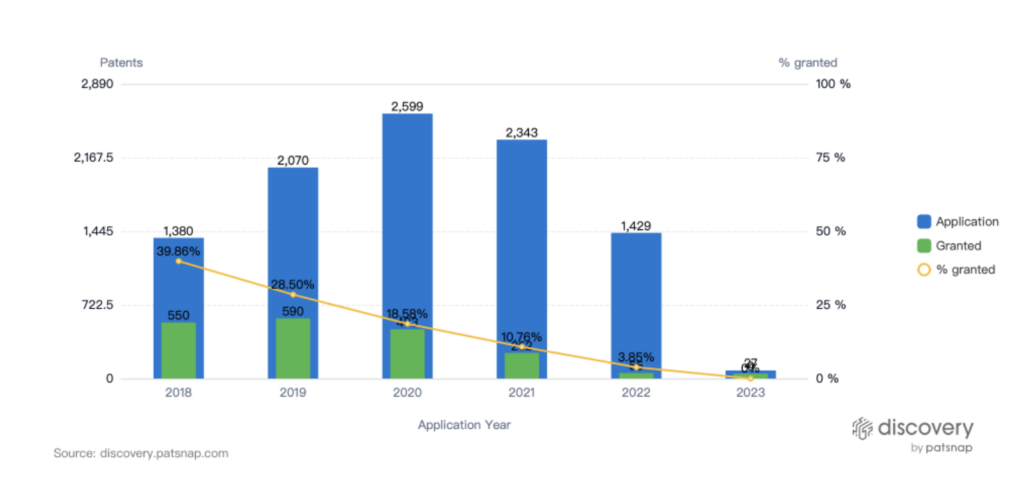
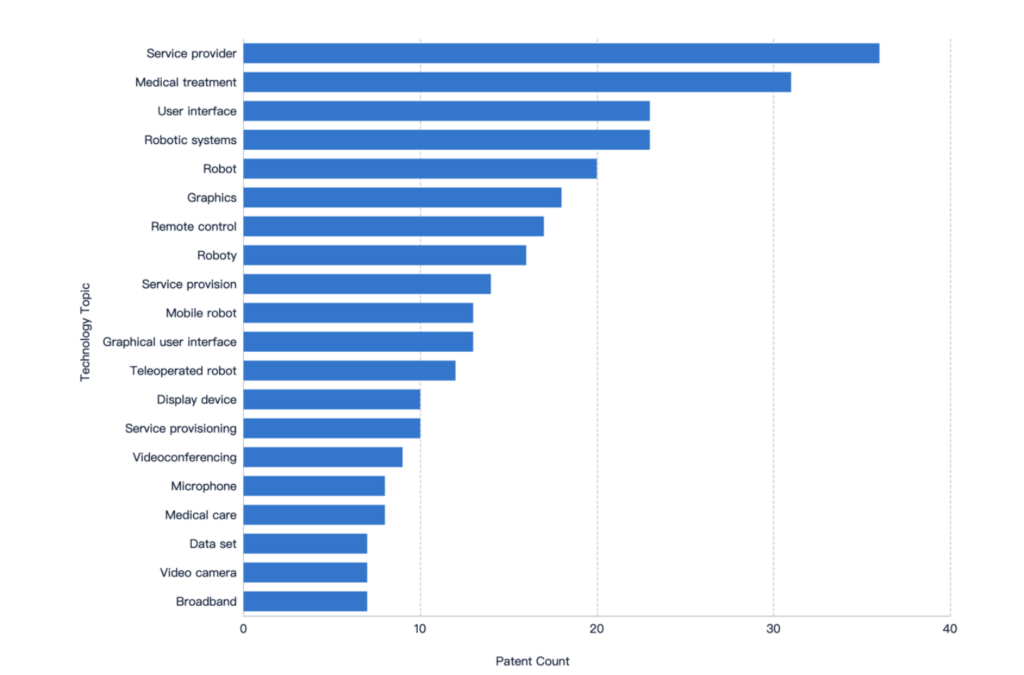
The telemedicine sector is currently experiencing a surge in patent filings and innovation, as companies strive to distinguish themselves by creating proprietary technologies and novel methods for delivering remote healthcare services. Among the latest trends is the development of AI and machine learning algorithms for diagnosing medical conditions and providing personalized care.
Additionally, wearable devices and remote monitoring technologies are emerging as crucial areas of innovation in this sector. To enhance virtual consultations and remote care, companies are exploring the use of augmented and virtual reality technologies.
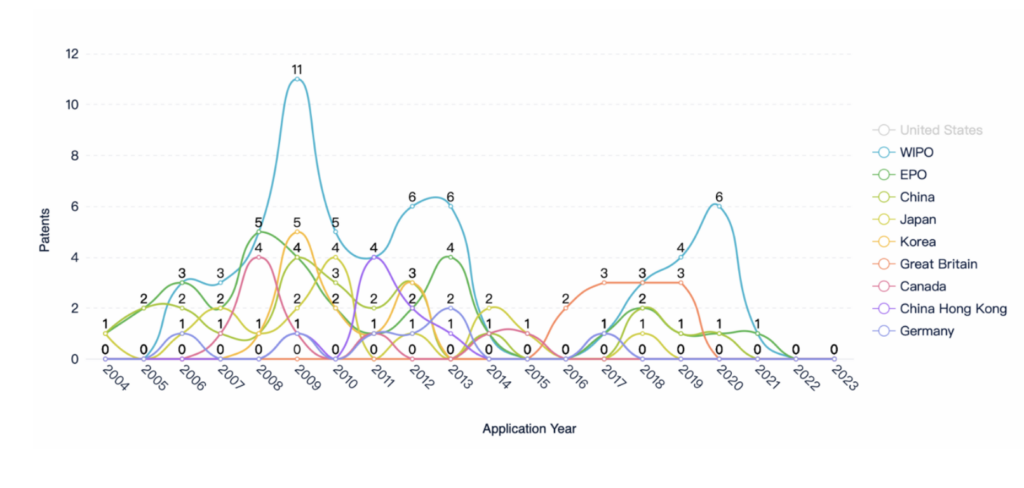
Patent filings reflect these innovation trends, with firms seeking patent protection for a wide range of telemedicine-related technologies and methods. As the industry continues to expand, innovation and patent filings are likely to remain key indicators of competition and differentiation in this rapidly evolving field. The COVID-19 pandemic has further accelerated the growth of the telemedicine industry, as illustrated by the significant surge in patent applications in 2020, as shown in the graph above.
Key Patent Filings
Telemedicine technologies, such as remote monitoring devices and mobile applications, may be eligible for patent protection. According to a recent report by IPWatchdog, patent filings in this sector have been steadily increasing over the past decade. In 2020 alone, more than 3,000 telemedicine-related patents were filed, representing a 25% increase from the previous year.
Many companies have filed patents for innovative technologies and methods for delivering remote healthcare services. For example, Teladoc, one of the leading telemedicine providers, filed patents related to virtual medical consultations, remote diagnosis, and treatment planning. Another notable company, Doctor on Demand, patented technologies for video consultations and remote monitoring of patient vital signs. As the graphs below illustrate, cumulative funding is on the rise for both Teladoc and Doctor on Demand.
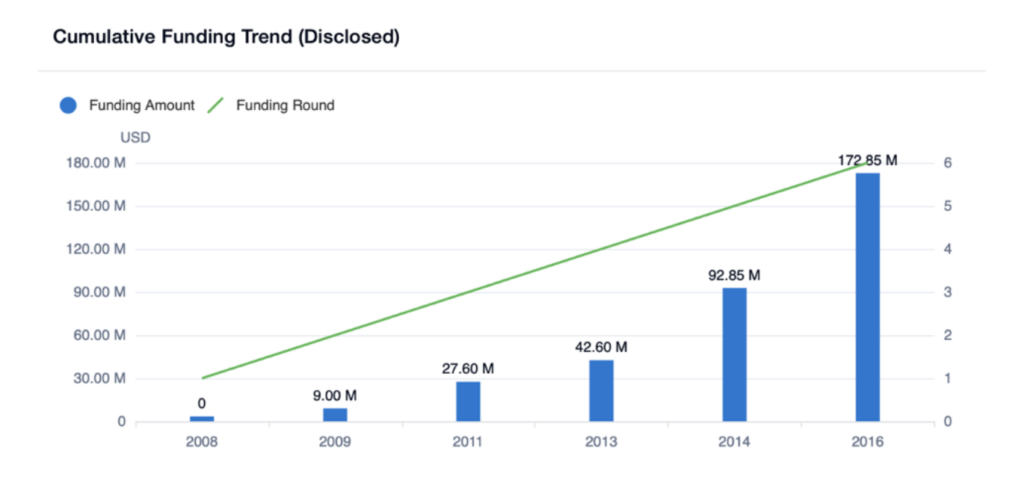
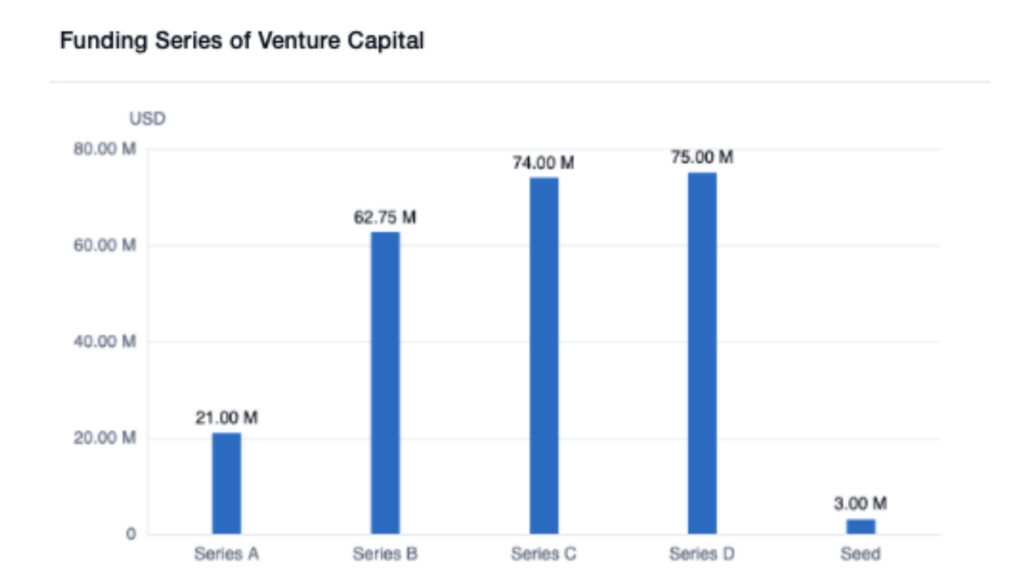
Major players such as IBM and Google have also submitted patent applications for various telemedicine-related technologies, such as machine learning algorithms for diagnosing medical conditions and wearable devices for monitoring patients remotely.
These patent filings reflect a substantial degree of innovation and competition within the industry, with companies striving to set themselves apart through their proprietary technologies and methods of delivering care. As this sector continues to expand, patent filings are expected to remain a crucial gauge of innovation and competition in the field.
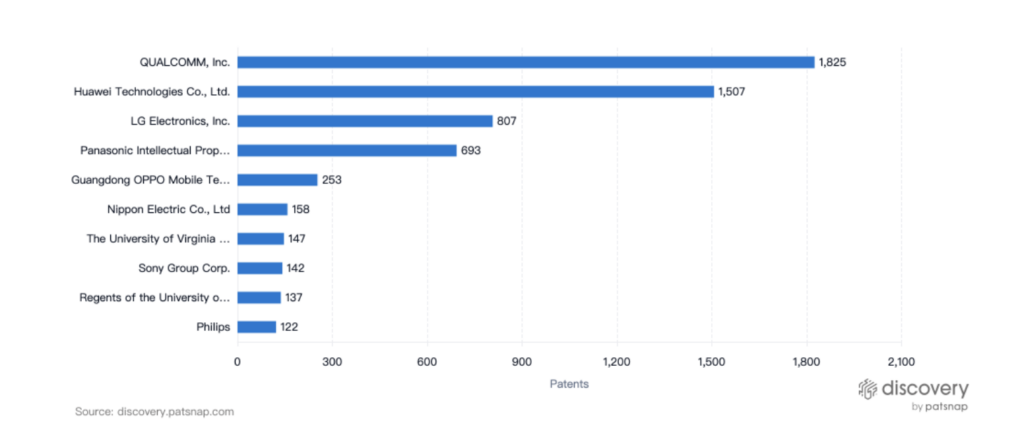
Leading Patent Filers
Given the funding insights shared above, it’s not surprising that both Teladoc and Doctor on Demand are at the forefront of telemedicine patent filings. Other key players include Amwell, and leading technology companies such as QUALCOMM, Huawei, and LG.
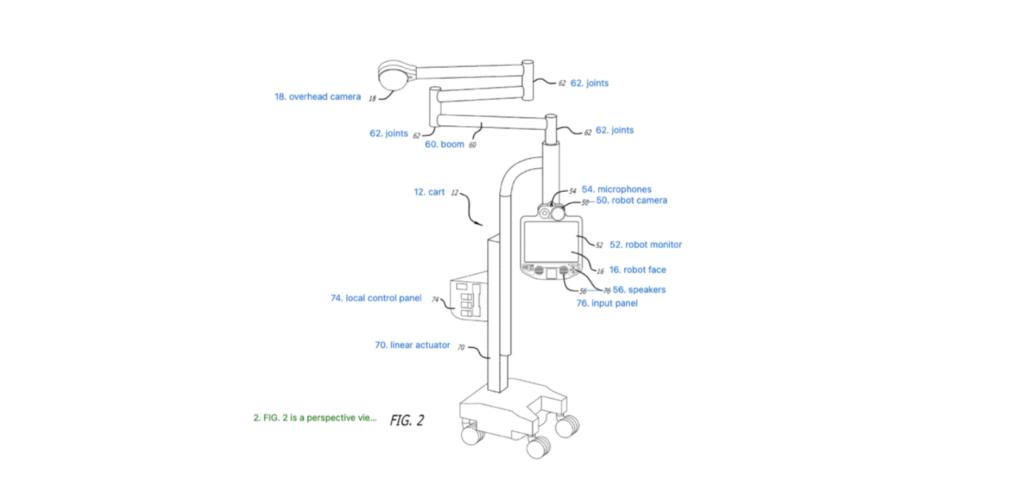
Filing patents in the telemedicine industry requires a thorough understanding of the nuanced technologies and methods used in remote healthcare services. Some specific examples of telemedicine patents include Teladoc’s patent for a “Remote presence system including a cart that supports a robot face and an overhead camera” (patent US20210074423A1), which describes a system for facilitating virtual consultations between patients and healthcare providers.
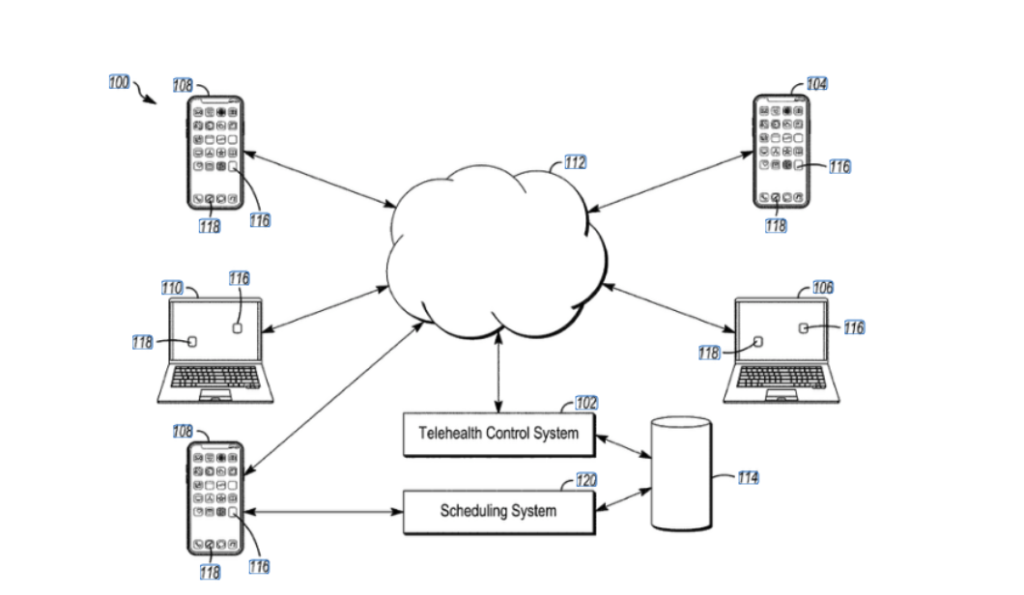
Tenovi’s patent for “Systems and Methods for Remote Patient Monitoring” (patent US20230013837A1) offers another example of innovation in the telemedicine sector. This patent outlines a technique for remotely monitoring patients’ vital signs via wearable devices and transmitting the data to healthcare providers.
Several other noteworthy telemedicine patents exist, including MDLive’s patent for “Telehealth control system and method for engaging providers” (US20220367045A1), which describes a system for delivering remote medical services across multiple platforms, and Verizon Patent & Licensing’s patent for “System and Method for Providing Remote Health Care Services” (US9974485B2), which details a method for managing patient health records and conducting remote consultations. These patents illustrate the vast range and diversity of telemedicine-related technologies and methods, highlighting the significance of safeguarding intellectual property in this rapidly growing industry.
Telemedicine Competitive Analysis
Leading telemedicine providers include Teladoc, Amwell, Doctor on Demand, MDLive, and Babylon Health. These companies differentiate themselves through branding, pricing, and the quality of their services.
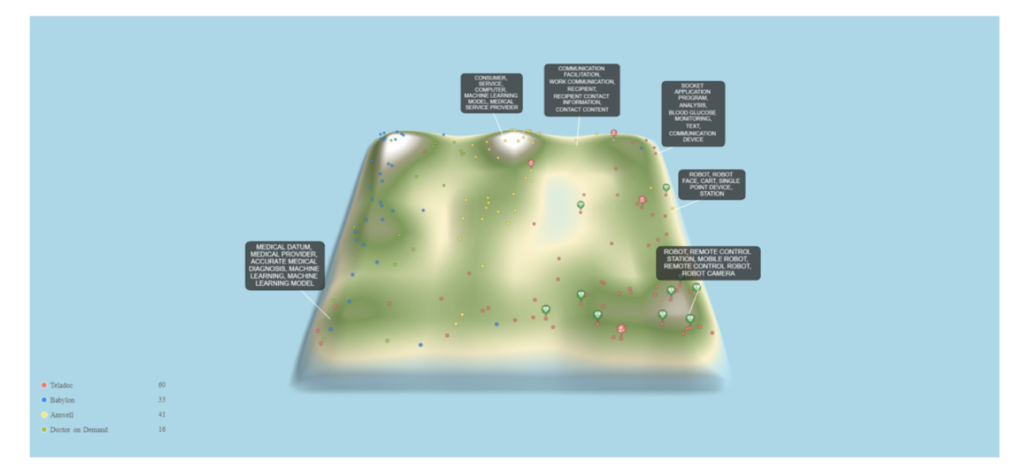
For example, Babylon Health offers AI-based triage and diagnosis services in addition to virtual consultations, while Teladoc and Doctor on Demand have developed partnerships with major healthcare systems and insurers to expand their reach.
Kry and Zava are among the leading telemedicine providers in Europe, delivering a variety of virtual healthcare services across several countries. Meanwhile, telemedicine firms such as Ping, A Good Doctor, and AliHealth have seized opportunities in the expanding Chinese market, as the demand for remote healthcare services in the region continues to rise.
Although the international telemedicine sector confronts obstacles like regulatory barriers and technological constraints, companies that can navigate these challenges and differentiate themselves through their technology and services are well-positioned to thrive in the global telemedicine market. As telemedicine gains further traction worldwide, competition is anticipated to intensify, with companies striving to gain market share.
Limitations of Telemedicine
Despite the potential benefits of telemedicine, the field faces several limitations. These limitations include regulatory barriers, reimbursement issues, and technological challenges.
Limitation #1: Regulatory Burdens
State and federal laws regulate the use of telemedicine, which can be intricate and subject to variations depending on the type of service rendered. This may generate uncertainty for telemedicine providers and restrict the availability of services in specific states. To guarantee the expansion and viability of the telemedicine industry, companies such as Teladoc have advocated for enhanced regulation and clarity.
Limitation #2: Reimbursement Issues
Telemedicine services are often not reimbursed at the same rate as in-person medical services. This can make it difficult for providers to offer telemedicine services and can limit the availability of services to patients. For example, Medicare only reimburses for telemedicine services under certain circumstances, which can create financial barriers for providers and patients.
International Trends
Telemedicine trends differ by jurisdiction, with each region experiencing distinct growth patterns and obstacles. In the United States, telemedicine adoption has rapidly expanded in recent years, fueled in part by the demand for remote care during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, telemedicine regulations remain intricate and differ by state, and some states still restrict reimbursement for telemedicine services.
In Europe, telemedicine adoption has been sluggish due to fragmented regulations and cultural disparities in healthcare delivery. Nevertheless, the European Union is taking measures to promote telemedicine adoption, including financing initiatives to support telemedicine infrastructure and encouraging cross-border healthcare services. In Asia, telemedicine is witnessing swift growth due to the necessity of providing care to a large and aging population. Whereas in countries such as China and India, telemedicine is being leveraged to tackle the shortage of healthcare providers in rural areas.
Telemedicine Holds Limitless Potential
To sum up, telemedicine is a rapidly expanding domain that holds the potential to expand access to healthcare services and reduce costs. Over the past decade, patent filings in telemedicine have steadily increased, indicating potential for augmented innovation and competition in the field. Leading telemedicine providers such as Teladoc, Amwell, and Doctor on Demand have obtained patents for their technologies and distinguished themselves through branding, pricing, and service quality.
However, the sector still encounters limitations, such as regulatory barriers, reimbursement issues, and technological challenges. Tackling these limitations will be critical to the continued growth and prosperity of the telemedicine industry. In general, telemedicine offers an encouraging prospect to revolutionize the healthcare industry and enhance patient outcomes.